はじめに
この記事では「グローバル変数」と「ローカル変数」についてと、「Serializefield」を使ったInspectorを表示方法を紹介しています。
― YouTubeなら2分43秒で学べます ―
ローカル変数について
ローカル変数は「メソッド内で定義された変数」のことで、そのメソッド内でしか使うことができません。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 |
using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; using UnityEngine; public class Test : MonoBehaviour { // Use this for initialization void Start() { int local = 1; Debug.Log("local:"+ local); } // Update is called once per frame void Update() { //別のメソッド内では利用できません //Debug.Log("local:"+ local); } } |
|
1 2 3 |
実行結果 local:1 |
グローバル変数について
グローバル変数では、そのクラス内であれば、どのメソッドからでも参照できます。
基本的な法則として、変数は { } で囲った中であれば共通して利用することができます。
例えば、ローカル変数はメソッド内での定義なので、メソッド内でしか使えませんが、グローバル変数はクラス内での定義ですので、クラス内のメソッド全てに適用できます。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 |
using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; using UnityEngine; public class Test : MonoBehaviour { int global = 100; // Use this for initialization void Start() { Debug.Log("global:" + global); } // Update is called once per frame void Update() { } } |
|
1 2 3 |
実行結果 global:100 |
グローバル変数とローカル変数の優先度と「this」の使い方
ローカル変数とグローバル変数が同じ名前だった場合、ローカル変数が優先されます。
同名のローカル変数とグローバル変数が混在している場合、「this.変数名」を付けてあげると、このクラスの変数、つまり、「グローバル変数」が優先されます。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 |
using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; using UnityEngine; public class Test : MonoBehaviour { int global = 100; // Use this for initialization void Start() { int global = 1; Debug.Log("ローカル変数のglobal:" + global); Debug.Log("グローバル変数のglobal:" + this.global); } // Update is called once per frame void Update() { } } |
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
実行結果 ローカル変数のglobal:1 グローバル変数のglobal:100 |
別クラスからpublic変数を参照する方法
別クラスからの参照を可能にする場合は、「public 型名 変数名」のように宣言してください。メソッド名の頭についていたpublicの正体はこれです。
別クラスから参照する方法は、「クラス名 変数名 = new クラス名()」のようにインスタンス化した後、「変数名 . 変数」のように呼び出します。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 |
using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; using UnityEngine; public class AnotherTest : MonoBehaviour { //別クラスからの参照を可能にするにはpublic public int anotherGlobal = 1000; } public class Test : MonoBehaviour { // Use this for initialization void Start() { //AnotherTestクラスをインスタンス化して参照 AnotherTest aTest = new AnotherTest(); Debug.Log("anotherGlobal" + aTest.anotherGlobal); } // Update is called once per frame void Update() { } } |
インスペクター上からpublic変数を上書きする方法
public変数はインスペクター上で書き換えることができます。しかも、Unityではインスペクター上の数字が優先されます。
例えば、「public int a = 1000」とグローバル変数で宣言しても、インスペクター上で「0」と上書きすると、「a = 0」となります。
なので、void Start()メソッドなどで「a = 100」ともう一度上書きする必要があります。
こういった理由から、勝手に書き換えられたくない場合はインスペクター上に表示しないようにしましょう。
インスペクター上の値を変更していないとき
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 |
using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; using UnityEngine; public class Test : MonoBehaviour { public int global = 1000; // Use this for initialization void Start() { Debug.Log("上書きされた変数" + global); global = 1000; Debug.Log("修正後の変数" + global); } // Update is called once per frame void Update() { } } |
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
実行結果 上書きされた変数:1000 修正後の変数:1000 |
インスペクター上の値を変更したとき
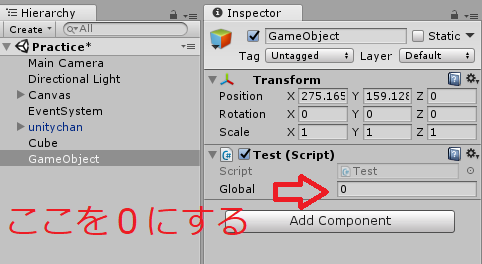
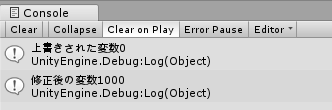
別クラスからのアクセスを禁止するprivate変数
別クラスからの参照を禁止するには「private 型名 変数名」のように宣言してください。
「型名 変数名」のように宣言した場合も、private変数の扱いになります。
public変数の場合、別クラスから変数を自由に書き換えることができるので、キャラの攻撃力を-100のようにするなど、ありえない数字を代入される恐れがあります。
また、private変数はインスペクターに表示されないので、エディタ上からの変更もされなくなります。
そういった理由から、変更されたくない値はprivate変数として宣言してください。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 |
using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; using UnityEngine; public class AnotherTest : MonoBehaviour { //別クラスからの参照を禁止するにはprivate private int anotherGlobal = 1000; } public class Test : MonoBehaviour { // Use this for initialization void Start() { //AnotherTestクラスをインスタンス化して参照 AnotherTest aTest = new AnotherTest(); //Debug.Log("anotherGlobal" + aTest.anotherGlobal); } // Update is called once per frame void Update() { } } |
|
1 2 3 |
実行結果 アクセスできない保護レベルになっています |
「Serializefield」を使ってprivate変数をインスペクターに表示する方法
private変数をインスペクター上から確認したいときは「 [Serialisefield] private クラス名 変数名」のように宣言してください。
private は無くてもエラーにはなりません。
これは、別クラスからの参照はして欲しくないが、実行中にどのような値が代入されているのかを目視したいときに使います。
public変数と同様、インスペクター上で値を変更すると、値が上書きされてしまうので注意が必要です。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 |
using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; using UnityEngine; public class Test : MonoBehaviour { [SerializeField] private int global = 1000; // Use this for initialization void Start() { } // Update is called once per frame void Update() { } } |
関連記事
ローカル変数の型名の宣言が楽になります。

外部オブジェクトに取り付けたクラスの変数を参照する方法です。


